- Xdebug Chrome
- Chrome Xdebug Helper
- Chrome Xdebug Enabler
- Chrome Xdebug Download
- Chrome Xdebug Not Working
Xdebug helper插件使用方法 1.在chrome浏览器安装好后,在浏览器的右上方会出现Xdebug helper插件的按钮。选择Debug,就会通知你的开发环境接下来的代码需要开始调试, 2.选择disable,就会直接运行。如下图所示:. XDebug Helper for Google Chrome Debugging, profiling and tracing PHP code with Xdebug is very powerful, but enabling Xdebug with cookies or adding POST/GET variables is way too hard. This extension will help you to enable/disable debugging, profiling and tracing of your PHP-code easily.
- Navigation
- Main Page
- Community portal
- Current events
- Recent changes
- Random page
- Help
- Toolbox
- Page information
- Permanent link
- Printable version
- Special pages
- Related changes
- What links here
- 2Setup
- 3Usage
About Xdebug
Xdebug is an opensource Debugger and Profiler for PHP. PDT has built in support for Xdebug, which allows you to step-debug through your PHP projects.
Setup
Installation
The first step is to install Xdebug and verify that Xdebug is running. See the Installation section of the Xdebug manual for how to obtain the extension.
To setup Xdebug as your default debugger in PDT, simply configure the Default Settings in the Debug eclipse preference page of PHP
Configuration
The most important setting for Xdebug to work with PDT is xdebug.remote_enable = 1. Typically you set this value in your php.ini. To verify that Xdebug
is loaded by your server, use the phpinfo() method and check if you can find an Xdebug configuration section.
Usage
The following examples assume you're debugging on a local mashine, not a remote server.
Debugging using the default DocumentRoot (http://localhost)
PDT provides a preference dialog to configure different PHP servers.
Each server has has a Base URL and a Local Web Root property.
When you start a debug session, the Base URL is used in conjunction with the path of the script you're debugging to determine the absolute URL to open. For example, when you debug
the script index.php in the root of your Project with the default PHP Server, PDT will launch a debug session in a browser with the URL http://localhost/index.php.
If the Local Web Root property of a server is set, you can choose the Server as the base-directory in the New PHP Project dialog (see screenshot below).
Typically you will set the Local Web Root of the default PHP server (http://localhost) to the DocumentRoot of your local Web server (e.g. apache).
The default PHP server is http://localhost and has no Local Web Root set. So the first thing to do is to open the PHP Servers preference page, and set the Local Web Root to the DocumentRoot
of your webserver (e.g. /var/www/htdocs).localhost
When creating a new PHP project, you will now see a 3rd option named Create project on local server. The new project will be created in a subfolder of the Local Web Root of the selected server, not
in the default workspace path:
Now let's create a new empty PHP project named 'MyProject' in the default PHP server and a simple index.php in the root of the project. To debug your script, all you need to do is right-clicking the index.php file and select Debug as -> PHP Web Application.
This will launch the default workbench browser with the URL http://localhost/MyProject/index.php and stop at the first line index.php (this is configurable via the Debug configuration):
You can set a breakpoint in the editor on any line by double clicking on a line number on the left.
Use Step Into (F5), Step Over (F6), Step Out (F7) or Resume (F8) to go through your scripts step by step.
Notice that the debugging session will still be open after pressing F8 (Resum), so you simply need to refresh the browser to restart debugging your script.
Debugging using VirtualHosts (http://myProject.local)
If you're using VirtualHosts for your local project, you need to configure a PHP Server first. This server simply needs to have the correct URL to your project, and the path to the Document root (Preferences -> PHP -> PHP Servers):
After you've setup the PHP server, you can create a new debug configuration (Run -> Debug Configurations -> PHP Web Application) using the newly created server:
Now you can simply click 'Debug' and the debug session should open in your browser.
Choosing the browser to use for debugging
By default, eclipse launches the debug session inside the internal browser. It is recommended to use an external browser though. You can specify the browser to use in the general preferences:
Perspectives
Eclipse may be configured to open the Debug perspective automatically or to get back to the PHP perspective automatically, but not both (see bug 46336).
Xdebug is an extension for debugging your PHP. The following explains how to configure Xdebug and PhpStorm to debug in your local environment. You can use the IDE of your choice. See the vendor documentation for those applications for further configuration information.
You can configure Xdebug to run in the Magento Cloud Docker environment for local debugging without changing your Magento Commerce Cloud project configuration. See Configure Xdebug for Docker.
To set up Xdebug, you need to configure a file in your Git repository, configure your IDE, and set up port forwarding. You can configure settings in the magento.app.yaml file. After editing, you can push the Git changes across all Starter environments and Pro Integration environments to enable Xdebug. To push these settings to Pro plan Staging and Production environments, you must enter a ticket.
Once configured, you can debug CLI commands, web requests, and code. Remember, all Magento Commerce Cloud environments are read-only. You need to pull code to your local development environment to perform debugging. For Pro Staging and Production environments, we include additional instructions for Xdebug.
Requirements
To run and use Xdebug, you need the SSH URL for the environment. You can locate the information through the Project Web Interface or your Cloud Onboarding UI.
Configure Xdebug
To configure Xdebug, you need to do the following:
- Work in a branch to push file updates
- Configure your IDE, like PhpStorm
For configuring on Pro plan Staging and Production, you need to enter a ticket for Staging and Production.
Get started with a branch
To add Xdebug, we recommend creating a branch to work in and add the files.
To get started with environment branches:
On your local workstation, change to your Cloud project directory.
Switch to the Magento file system owner.
Log in to your Magento project.
List your projects.
List environments in the project. Every environment includes an active Git branch that contains your code, database, environment variables, configurations, and services.
It is important to use the
magento-cloud environment:listcommand because it displays environment hierarchies, whereas thegit branchcommand does not.Fetch origin branches to get the latest code.
Checkout, or switch to, a specific branch and environment.
Git commands only checkout the Git branch. The
magento-cloud checkoutcommand checks out the branch and switches to the active environment.You can create a new environment branch using the
magento-cloud environment:branch <environment-name> <parent-environment-ID>command syntax. It may take some additional time to create and activate a new environment branch.Use the environment ID to pull any updated code to your local. This is not necessary if the environment branch is new.
(Optional) Create a snapshot of the environment as a backup.
Enable Xdebug in your environment
To enable Xdebug for your project, add xdebug to the runtime:extensions section of the .magento.app.yaml file.
You can enable Xdebug directly to all Starter environments and Pro Integration environments. For Pro Staging and Production, you need to update this file and enter a Support ticket to have it enabled. We enable Xdebug on those environments for you.
To enable Xdebug:
In your local terminal, open the
.magento.app.yamlfile in a text editor.In the
runtimesection, underextensions, addxdebug. For example:Save your changes to the
.magento.app.yamlfile and exit the text editor.Add, commit, and push the changes to redeploy the environment.
When deployed to Starter environments and Pro Integration environments, Xdebug is now available. You should continue configuring your IDE. For PhpStorm, see Configure PhpStorm.
Configure PhpStorm
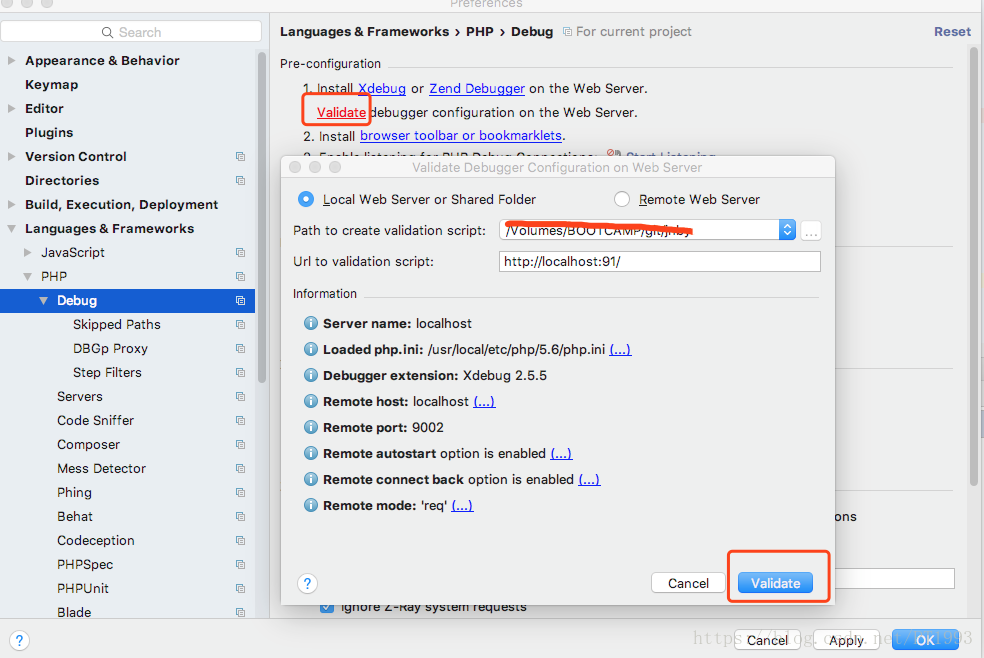
You need to configure PhpStorm to properly work with Xdebug.
To configure PhpStorm to work with Xdebug:
In your PhpStorm project, open the settings panel.
- Mac OS X—Select PhpStorm > Preferences.
- Windows/Linux—Select File > Settings.
In the Settings panel, expand and locate the Languages & Frameworks > PHP > Servers section.
Click the + to add a server configuration. The project name is in grey at the top.
Configure the following settings for the new server configuration:
- Name—enter the same as the hostname. This value is used in and must match the value for
PHP_IDE_CONFIGvariable in Debug CLI commands. - Host—Enter
localhost. - Port—Enter
80. - Debugger—Select
Xdebug.
- Name—enter the same as the hostname. This value is used in and must match the value for
Select Use path mappings. In the File/Directory pane, the root of the project for the
serverNamedisplays.In the Absolute path on the server column, click (Edit) and add a setting based on the environment:
- For all Starter environments and Pro Integration environments, the remote path is
/app. For Pro Staging and Production environments:
- Production:
/app/<project_code>/ - Staging:
/app/<project_code>_stg/
- Production:
- For all Starter environments and Pro Integration environments, the remote path is
Change the Xdebug port to 9000 in the Languages & Frameworks > PHP > Debug > Xdebug > Debug Port panel.
Click Apply.
Set up port forwarding
You must map the XDEBUG connection from the server to your local system. To do any type of debugging, you must forward port 9000 from your Magento Commerce Cloud server to your local machine. See one of the following sections:
Xdebug Chrome
Port forwarding on Mac or UNIX
To set up port forwarding on a Mac or in a Unix environment:
Open a terminal.
Use SSH to establish the connection.
Add the
-voption to the SSH command to show in the terminal whenever a socket is connected to the port that is being forwarded.If an “unable to connect” or “could not listen to port on remote” error is displayed, there could be another active SSH session persisting on the server that is occupying port 9000. If that connection isn’t being used, you can terminate it.
To troubleshoot the connection:
Use SSH to log in to the remote Integration, Staging, or Production environment.
Enter
whoto view a list of SSH sessions.View existing SSH sessions by user. Be careful to not affect a user other than yourself!
- Integration: usernames are similar to
dd2q5ct7mhgus - Staging: usernames are similar to
dd2q5ct7mhgus_stg - Production: usernames are similar to
dd2q5ct7mhgus
- Integration: usernames are similar to
For a user session that is older than yours, find the pseudo-terminal (PTS) value, such as
pts/0.Kill the process ID (PID) corresponding to the PTS value.
Sample response:
To terminate the connection, enter a kill command with the process ID (PID).
Port forwarding on Windows
To set up port forwarding (SSH tunneling) on Windows, you must configure your Windows terminal application. For this example, we walk through creating an SSH tunnel using Putty. You can use other applications such as Cygwin. For more information on other applications, see the vendor documentation provided with those applications.
To set up an SSH tunnel on Windows using Putty:
If you have not already done so, download Putty.
Start Putty.
In the Category pane, click Session.
Enter the following information:
- Hostname (or IP address) field: Enter the SSH URL for your Cloud server
- Port field: Enter
22
In the Category pane, click Connection > SSH > Tunnels.
Enter the following information:
- Source port field: Enter
9000 - Destination field: Enter
127.0.0.1:9000 - Click Remote
- Source port field: Enter
Click Add.
In the Category pane, click Session.
In the Saved Sessions field, enter a name for this SSH tunnel.
Click Save.
To test the SSH tunnel, click Load, then click Open.
If an “unable to connect” error displays, verify all of the following:
- All Putty settings are correct
- You are running Putty on the machine on which your private Magento Commerce Cloud SSH keys are located
Configure Pro Staging and Production
To complete configuration for Pro plan Staging and Production environments, you must enter a Support ticket to have Xdebug enabled and configured in Staging and Production environments.
We enable Xdebug in the environment. Be aware that this is a configuration change that requires us to redeploy your Staging and Production environments.
SSH access to Xdebug environments
For initiating debugging, performing setup, and more, you need the SSH commands for accessing the environments. You can get this information, through the Project Web Interface and your project spreadsheet.
Chrome Xdebug Helper
For Starter environments and Pro Integration environments, you can use the following Magento Cloud CLI command to SSH into those environments:
To use Xdebug, SSH to the environment as follows:
For example,
Debug for Pro Staging and Production
To use Xdebug specifically on Pro plan Staging and Production environment, you create a separate SSH tunnel and web session only you have access to. This usage differs from typical access, only providing access to you and not to all users.
You need the following:
- SSH commands for accessing the environments. You can get this information, through the Project Web Interface or your Cloud Onboarding UI.
- The
xdebug_keyvalue we set when configuring the Staging and Pro environments
To set up an SSH tunnel to a Staging or Production environment:
Open a terminal.
Clean up all SSH sessions.
Set up the SSH tunnel for Xdebug.
To start debugging using the environment URL:
To enable remote debugging, visit the site in the browser with the following added to the URL where
KEYis value forxdebug_key:This sets the cookie that sends browser requests to trigger Xdebug.
Complete your debugging with Xdebug.
When you are ready to end the session, you can use the following command to remove the cookie and end debugging through the browser where
KEYis value forxdebug_key:The
XDEBUG_SESSION_STARTpassed byPOSTrequests are not supported at this time.
Debug CLI commands
Chrome Xdebug Enabler
This section walks through debugging CLI commands.
To debug CLI commands:
SSH into the server you want to debug using CLI commands.
Create the following environment variables:
These variables are removed when the SSH session ends.
Begin debugging
On Starter environments and Pro Integration environments, run the CLI command to debug.You may add runtime options, for example:
On Pro Staging and Production environments, you must specify the path to the Xdebug php configuration file when debugging CLI commands, for example:
For debugging web requests
The following steps help you debug web requests.
On the Extension menu, click Debug to enable.
Right click, select the options menu, and set the IDE key to PHPSTORM.
Install the Xdebug client on the browser. Configure and enable it.
Example set up on Chrome

This section discusses how to use Xdebug in Chrome using the Xdebug Helper extension. For information about Xdebug tools for other browsers, consult the browser documentation.
To use Xdebug Helper with Chrome:
Create an SSH tunnel to the Cloud server.
Install the Xdebug Helper extension from the Chrome store.
Enable the extension in Chrome as shown in the following figure.
In Chrome, right-click in the Chrome toolbar.
From the pop-up menu, click Options.
From the IDE Key list, click PhpStorm.
Click Save.
Open your PhpStorm project.
In the top navigation bar, click (Start listening).
If the navigation bar isn’t displayed, click View > Navigation Bar.
In the PhpStorm navigation pane, double-click the PHP file to test.
Chrome Xdebug Download
Debug code locally
Due to the read-only environments, you need to pull code locally from an environment or specific Git branch to perform debugging.
The method you choose is up to you. You have the following options:
Check out code from Git and run
composer installThis method works unless
composer.jsonreferences packages in private repositories to which you do not have access. This method results in getting the entire Magento codebase.Copy the
vendor,app,pub,lib, andsetupdirectoriesThis method results in your having all code you can possibly test. Depending on how many static assets you have, it could result in a long transfer with a large volume of files.
Copy the
vendordirectory onlyBecause most Magento and third-party code is in the
vendordirectory, this method is likely to result in good testing although you will not be testing the entire codebase.
Chrome Xdebug Not Working
To compress files and copy them to your local machine:
Use SSH to login to the remote environment.
Compress the files.
For example, to compress the
vendordirectory only, enterOn your local environment, use PhpStorm to compress the files.
